Digital Transformation Lifecycle Explained
The Digital Transformation Lifecycle contains a set of phases in which each phase is interconnected with the before phase. It gives a highly useful sequence of phases and instructions Digital Transformation performer, executant. And also business analysts, internet architects as well as transformation experts can follow, in any case of industry or size of the organization.
Definition of digital transformation lifecycle
Digital transformation is a procedure of nonstop innovative change. Hence, the lifecycle is the name indicates, should also be a consecutive process of advancement. So, makes supervise you the instructions that could become complicated. Also, distribute clear, measurable results, adding notable business value to the organization.
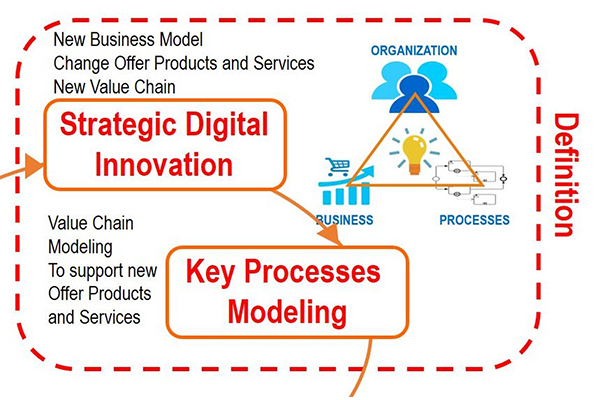
Step-1: Definition
A) Innovation stage:
A company significantly considers replacing large, heavily governed public sector IT teams with little. Lightly-public sector teams that can move and innovate much faster than replacing a vast amount of time, cost, and untested predictions. So, the teams should release scores of minimum viable products. Finally, let customer feedback guide improvement, scaling efforts up or down as proper.
B) Key processes:
The strategic and tactical outcomes are derived in the enterprise Architecture, the modification, rationalization, and simplification. The current business processes are prioritized, and the creation of the new key processes necessary for the rethinking.
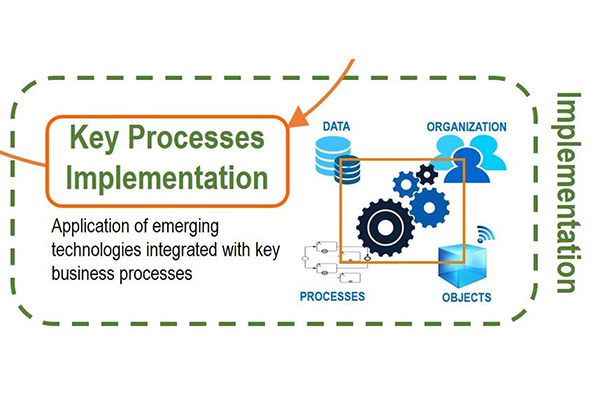
Step-2: Implementation
The models of the key processes, you need to implement the automation of business processes for execution in a BPM, bpm is a Workflow engine. In BPM contains four keys:
Data
Business information flowing through the process flow. In addition to the consuming information of the implementation of the process features by the BPM engine workflow.
Objects
Smart outcomes through sensors can send or receive events to respond with an action interacting with processes.
Organization
Management of the resources involved in the execution of the process, with dynamic allocation of participants according to roles.
Processes
It stores all relevant process flow data to optimally organize resources, control the execution of activities, assist in decision-making, respond to events. Besides measuring performance by managing processes based on time, cost, capacity, and quality.
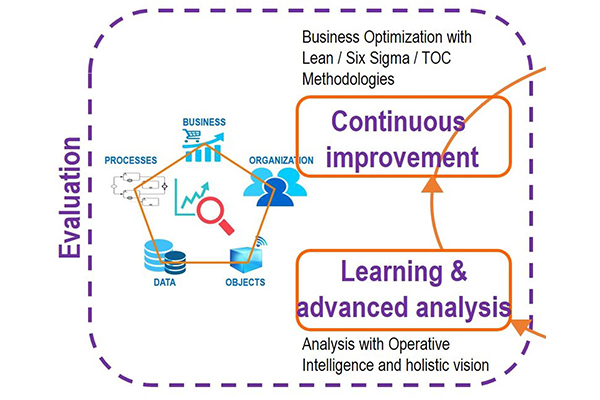
Step-3: Evaluation
A) Learning and analysis
The theme of rapid fast is to continually develop the products and services provided to customers. Further, to do that, a company needs intelligence to iterate its current offerings. This is information about establishing feedback between consumers and the business. The business becomes proactive monitoring and analytics provide guidelines into how a company’s software is used.
B) Continuous improvement stage for business optimization
The approach for business optimization in an age of all-pervasive connectivity and proliferating devices. Then now, the riotous threats feed on far more than just the one or two industry laggards.
Applications of digital transformation lifecycle
Social media
The way of use is much more inclusive than extremely delivering related content to your target audience. For example, noticing customer interactions to detect their activities, desire, and even respond to crises rapidly.

Government and the public sector
From the citizen, experience perspective the role of the digital transformation lifecycle becomes clear. So, the e-government and digital identity programs. In addition to many other area’s transparencies, efficiency, and finally, coordination is key in the digitization of processes and project management.
Insurance industry
Most consumers, for instance, be willing to have a sensor-based car or home if this would to like result in a reduction in premiums. And then, most technologies offer tremendous opportunities increasingly insurers are also challenges.

Healthcare
Mobile devices totally changed the face of healthcare. Increasing productivity and employee satisfaction is another challenge. Doctors, specialists, and nurses often have to work in increasingly difficult circumstances amidst budget cuts.

Banking
Most several changes, disruptions, and digital transformation challenges in retail banking are restricted to specific geographies provident, for instance regulatory, consumer-related, focus-related, and even broader societal elements.
Internet of things
Given the aforementioned changing landscape, real-time consumer feedback is one of the significant components of success available to retailers, consumer goods companies, the automotive sector, and more. A large development in implementing a PLM (Product Lifecycle Management) digital strategy is considering the Internet of Things (IoT) and its helpful effects.
Summary
It established different aspects of the digital transformation phases. Some of the impacts discussed in the theory can therefore be fulfilled with the digital transformation lifecycle model and help improve the current high failure rate in the industry. In future discussions, this will be extended to evidence deeper insights into aspects such as digital transformation ontology and algorithms, digital transformation architecture, and multiple agile modeling disciplines such as value cost-based revenue, performance, or service modeling.







Leave A Comment
You must be logged in to post a comment.